What Does Stream Attenuation Mean?: Understanding Its Impact
Stream attenuation refers to the reduction of water flow and energy in a stream. This process is vital for maintaining healthy waterways and ecosystems.
Understanding stream attenuation helps us manage water resources better. It involves natural and human-made factors that slow down water flow. These factors can include vegetation, soil types, and man-made structures. By learning about stream attenuation, we can improve flood control, water quality, and habitat protection.
This knowledge is crucial for engineers, environmentalists, and anyone interested in preserving our water systems. Let’s dive deeper into what stream attenuation means and why it matters.
Introduction To Stream Attenuation
Understanding stream attenuation is crucial for anyone studying water systems. It refers to the process of reducing the force or impact of a stream. This can happen naturally or through human intervention.
Stream attenuation helps manage water flow and prevents flooding. It also plays a role in preserving aquatic habitats. Let’s explore what it means and why it’s important.
Definition
Stream attenuation is the slowing down or reduction of water flow. This can occur due to natural barriers like rocks and vegetation. Human-made structures such as dams and levees can also attenuate streams.
Attenuation helps control the volume and speed of water moving downstream. It is essential for maintaining the health of a stream ecosystem.
Importance
Stream attenuation is vital for flood management. By reducing water flow, it lowers the risk of flooding. This protection is crucial for communities living near water bodies.
Attenuation also helps maintain water quality. Slower-moving water reduces erosion and sediment buildup. This keeps the stream clear and healthy for wildlife.
Preserving aquatic habitats is another benefit. Attenuated streams provide stable environments for fish and plants. This stability supports biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Natural Factors
Stream attenuation refers to the reduction of the peak flow rate in a stream. Natural factors play a crucial role in this process. They help regulate water flow, ensuring a stable and healthy ecosystem.
Geological Features
Geological features significantly impact stream attenuation. The type of soil, rock formations, and landscape shape water movement. Permeable soils, like sand, allow water to infiltrate. This reduces surface runoff.
Rock formations can create natural barriers. These barriers slow down the water flow. Valleys and slopes also influence how water travels. Steeper slopes lead to faster flows. Gentle slopes promote slower, more controlled movement.
Vegetation
Vegetation is another essential factor. Plants and trees absorb water through their roots. This reduces the amount of water that reaches the stream. Leaves and branches intercept rainfall. This process is known as canopy interception.
Roots also stabilize the soil. They prevent erosion and reduce sediment in the water. Vegetation along stream banks provides shade. This helps maintain cooler water temperatures, which is vital for aquatic life.
Human Influences
Human influences play a critical role in stream attenuation. Various human activities impact the natural flow and quality of streams. Understanding these influences helps in managing and protecting water resources.
Urbanization
Urbanization significantly alters the natural landscape. It leads to increased impervious surfaces like roads and buildings. These surfaces prevent water from infiltrating the ground. The result is more runoff and less groundwater recharge. Increased runoff can cause higher stream flows during storms. This can lead to erosion and sedimentation. Pollution from urban areas also affects water quality. Chemicals, oils, and waste enter streams through runoff. This harms aquatic life and reduces water quality.
Agricultural Practices
Agricultural practices also influence stream attenuation. The use of fertilizers and pesticides can lead to runoff. These chemicals enter streams and affect water quality. Excess nutrients from fertilizers cause algal blooms. This reduces oxygen levels in the water and harms fish. Soil erosion from farming contributes to sediment in streams. Sediment can clog waterways and impact aquatic habitats. Livestock access to streams can also be problematic. Animals can erode stream banks and contaminate water with waste.
Measurement Techniques
Understanding stream attenuation is vital for managing water resources. Accurate measurement techniques are essential to assess how streams reduce the energy of flowing water over distance. Let’s dive into two main methods: field measurements and modeling approaches.
Field Measurements
Field measurements involve collecting data directly from the stream. This can be done using various instruments such as flow meters and water quality sensors.
For instance, you might use a flow meter to measure the velocity of the water at different points along the stream. This data helps you understand how quickly the stream is losing energy.
Field measurements provide real-time data. However, they can be labor-intensive and require regular monitoring.
Modeling Approaches
Modeling approaches use computer simulations to predict how streams behave under different conditions. These models can incorporate numerous variables such as rainfall, terrain, and vegetation.
Using software, you can simulate various scenarios and see how changes in one factor might affect stream attenuation. For example, adding vegetation along the stream can slow down water flow, reducing energy loss.
Modeling is less labor-intensive than field measurements. However, it requires accurate input data and expertise to create reliable models.
So, which method is best for you? It often depends on your specific needs and resources. Combining both can give you a more comprehensive understanding of stream attenuation.
Impact On Water Quality
Understanding stream attenuation is crucial for anyone interested in water quality. Stream attenuation refers to the natural process where a stream’s water flow slows down. This slowdown can have a significant impact on water quality, affecting everything from sediment transport to nutrient levels. Let’s dive into how stream attenuation influences these two critical areas.
Sediment Transport
Stream attenuation plays a big role in sediment transport. When water flow decreases, it loses the energy needed to carry sediment. This means more sediment settles at the bottom of the stream.
Why does this matter to you? Excess sediment can cloud the water, making it difficult for aquatic plants to get the sunlight they need. It can also smother fish eggs and other aquatic life. So, monitoring sediment levels is essential for maintaining a healthy stream ecosystem.
Have you ever noticed a stream after a heavy rain? The water is often murky due to increased sediment. But as the stream attenuates, the water clears up. This natural process is crucial for water quality.
Nutrient Levels
Nutrient levels are another aspect affected by stream attenuation. When water flow slows, nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus can accumulate. These nutrients are essential for plant growth, but too much can cause problems.
Excess nutrients can lead to algal blooms, which deplete oxygen in the water. This can create dead zones where aquatic life struggles to survive. Have you ever seen a pond covered in a green film? That’s often a result of nutrient overload.
Managing nutrient levels is vital for water quality. You can help by reducing fertilizer use in your garden or supporting local initiatives to control agricultural runoff. Small actions can make a big difference in maintaining healthy water ecosystems.
Stream attenuation is a complex but fascinating topic that has real-world implications. By understanding its impact on sediment transport and nutrient levels, you can take steps to protect and improve water quality in your area. What steps will you take today to make a difference?

Credit: www.ign.com
Ecosystem Consequences
Stream attenuation means the reduction of water flow speed in a stream. This process helps prevent erosion and flooding. It also supports aquatic life by creating stable habitats.
Stream attenuation impacts the environment in various ways. It alters the natural flow and speed of streams, leading to significant changes in the ecosystem. These changes can affect biodiversity, disrupt habitats, and lead to other ecological issues.Biodiversity
Stream attenuation can reduce biodiversity. Slower water flow limits the variety of aquatic species. Fish, insects, and plants depend on specific water conditions. Changes in flow can make survival difficult for them. This can lead to a decline in species diversity.Habitat Disruption
Changes in stream flow can disrupt habitats. Many species rely on specific water levels and temperatures. Altered flow can affect these conditions, making habitats unsuitable. This can force species to migrate or face extinction. The loss of habitats impacts the entire ecosystem. “`Management Strategies
Understanding stream attenuation is vital for maintaining healthy waterways. Management strategies play a critical role in reducing the negative impacts and ensuring that streams can sustain their natural functions. Let’s delve into two key strategies: restoration projects and regulatory policies.
Restoration Projects
Restoration projects aim to bring degraded streams back to their natural state. This can include activities like replanting native vegetation, removing invasive species, or reshaping the stream channel to its original form. Each of these steps helps to stabilize the stream banks and improve water quality.
In my community, a local stream was suffering from severe erosion. Volunteers came together to plant trees along the banks. Over time, these trees helped reduce erosion and improved the habitat for local wildlife. Simple actions like these can make a significant difference in stream health.
Regulatory Policies
Regulatory policies are essential for protecting streams from further harm. Governments can introduce laws to limit pollution, control water usage, and manage land development near streams. These policies ensure that everyone plays a part in protecting our waterways.
One effective policy example is the implementation of buffer zones around streams. These zones restrict certain activities, like construction or farming, within a specified distance from the stream. This helps to prevent contaminants from reaching the water and reduces the risk of erosion.
Have you ever thought about how your actions might impact a nearby stream? Simple choices, like proper disposal of waste and supporting local environmental regulations, can contribute to healthier waterways.
By combining restoration projects and regulatory policies, we can create a comprehensive approach to managing stream attenuation. These strategies are not just beneficial for the environment but also for our communities. What steps can you take today to support these initiatives?

Credit: orange.wateratlas.usf.edu
Future Research Directions
Stream attenuation refers to the reduction of the intensity or strength of a stream’s flow. It can occur due to natural or artificial barriers. Understanding its impact helps in managing water resources efficiently.
### Future Research Directions Understanding stream attenuation is crucial for managing water resources effectively. Future research in this area holds significant promise. We must focus on technological advancements and collaborative efforts. ### Technological Advancements Technological advancements in data collection and analysis are game changers. Real-time monitoring systems can track changes in water flow and quality with precision. Imagine using drones to map water bodies. They can gather data from remote areas, offering insights previously inaccessible. Machine learning can predict stream behavior. This helps in planning for floods and droughts, making communities safer. ### Collaborative Efforts Collaborative efforts are equally important. Researchers, policymakers, and local communities need to work together. I once participated in a community-led water conservation project. The local knowledge combined with scientific data made our efforts more effective. International partnerships can also yield great results. Sharing data and resources can lead to breakthroughs in stream attenuation research. How can you contribute to these collaborative efforts? Start by getting involved in local water conservation projects. Your input can make a difference. By focusing on these areas, we can advance our understanding of stream attenuation. This will help in managing our water resources better and ensuring a sustainable future.
Credit: www.reddit.com
Frequently Asked Questions
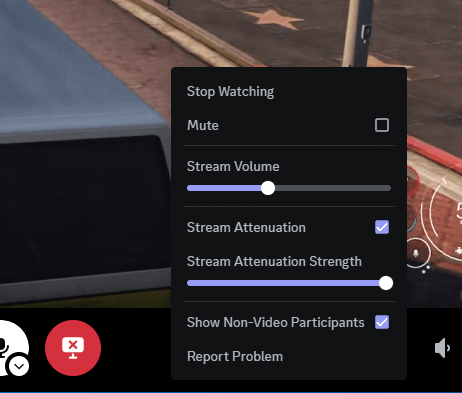
What Does Stream Attenuation Do On Discord?
Stream attenuation on Discord reduces the volume of other users when someone is speaking. This helps you hear better.
What Does It Mean When Attenuation Is Very High?
High attenuation means a significant loss of signal strength. It can affect communication quality and reduce data transmission efficiency.
Is Lower Attenuation Better?
Yes, lower attenuation is better. It means less signal loss over distances, resulting in better performance and reliability.
What Does 20 Db Attenuation Mean?
20 dB attenuation means a reduction in signal strength by 10 times. It measures the decrease in power or intensity.
Conclusion
Stream attenuation plays a vital role in waterway health. It reduces water flow speed. This process helps prevent flooding. It also controls soil erosion. Cleaner water results from this natural filtration. Understanding stream attenuation helps in water management. It benefits both nature and communities.
Simple practices can support this natural process. By doing so, we protect our environment. Everyone should learn about stream attenuation. It’s a small step with big impacts.